Covid clouds lens and cornea
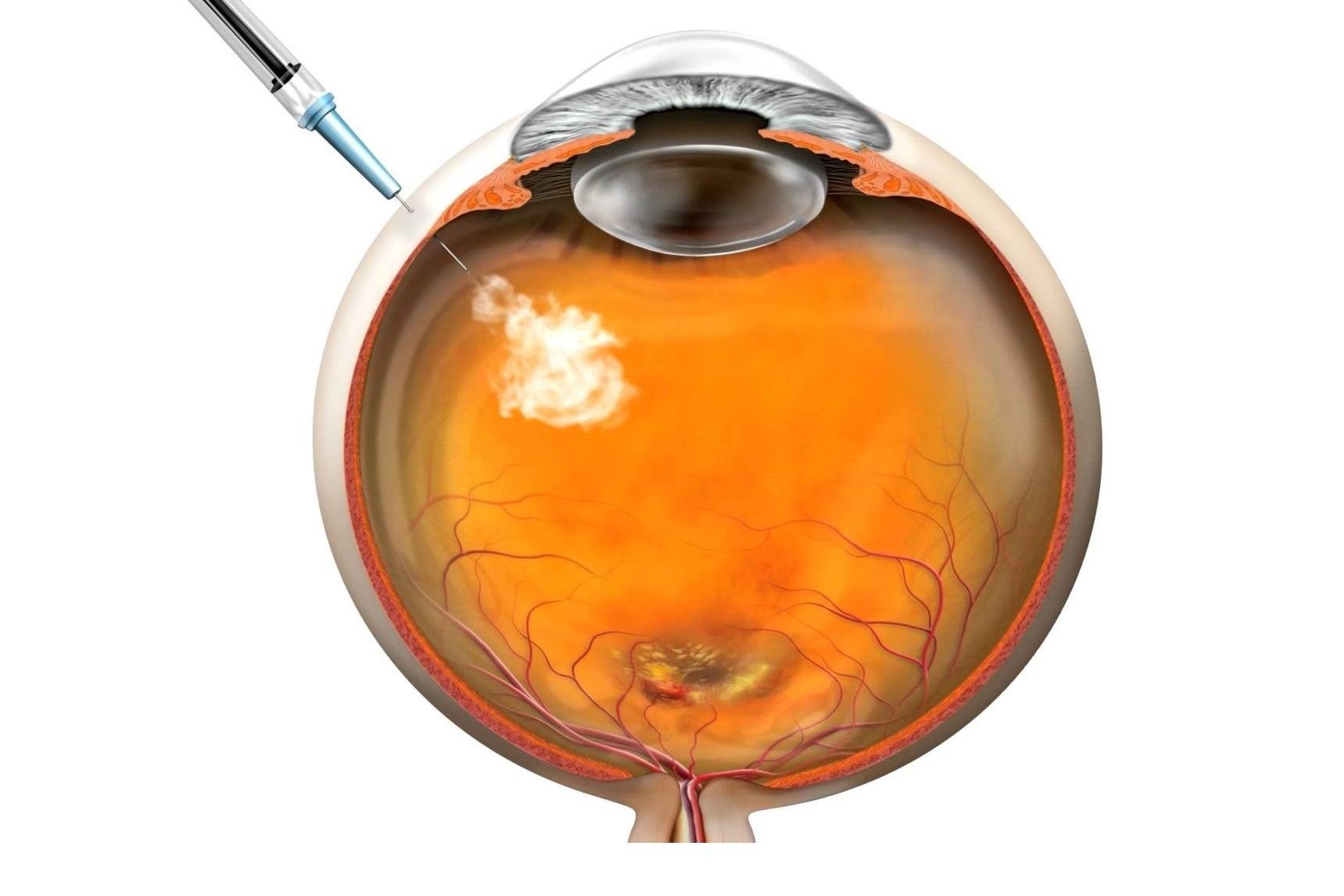
A Turkish study has shown that some patients had significant alterations in corneal and lenticular densitometric values following Covid-19 infection.
The study evaluated the corneal and lenticular clarity of 51 healthy individuals and 53 patients who had recovered from Covid-19. Compared to the control group, lens densitometry was significantly higher among patients in the Covid-19 group in all but one of the four corneal depth zones measured. The authors, led by Dr Emre Aydemir from the Adıyaman Training and Research Hospital, said the differences they found suggest Covid may have a global impact on the cornea, especially in the anterior layer and central zones, which could be due to ocular inflammation triggered by the increased systematic inflammatory burden.
The authors also noted Yuan et al’s 2020 discovery of Covid-19-binding ACE2 receptors in the cornea, conjunctiva and limbal regions, which could make the eye an alternative to the respiratory system as the virus’ portal into the body.