Mitomycin C after crosslinking increases corneal haze
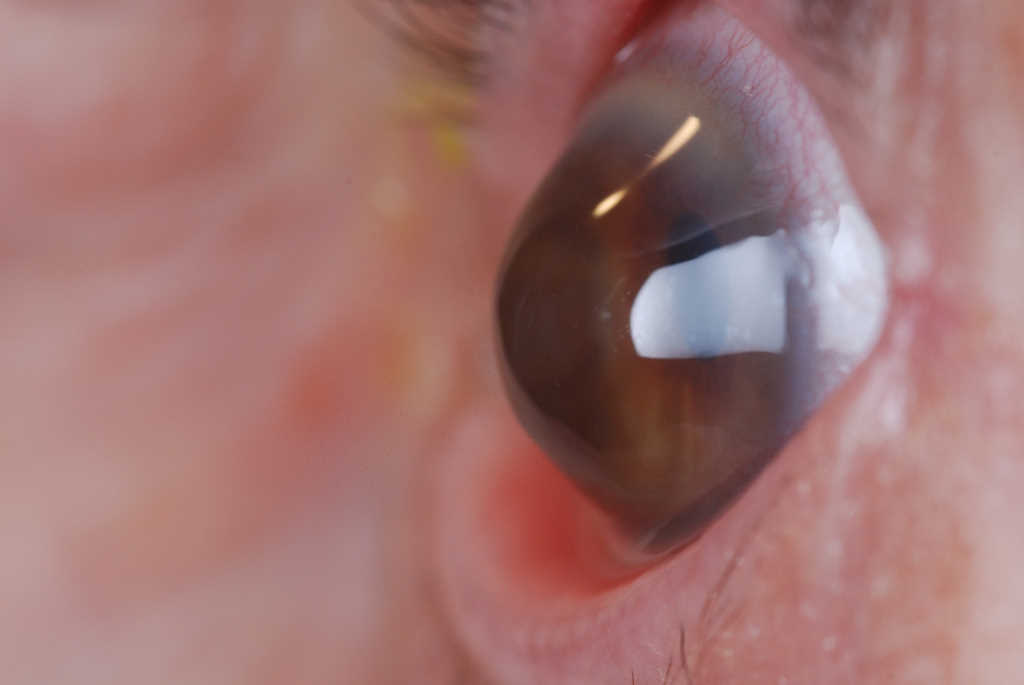
Mitomycin C (MMC), applied to inhibit incoming keratocytes after corneal crosslinking (CXL), increases corneal haze, according to the authors of a study in Lebanon.
Led by Professor Shady Awwad from the American University of Beirut Medical Center, Lebanon, the study included 72 patients (87 keratoconic eyes) who underwent CXL. Of these, 44 eyes underwent CXL and 43 eyes underwent CXL with MMC. Corneal haze, as evaluated by optical coherence tomography (OCT), was significantly higher in the MMC-treated group at one month and one year, postoperatively. However, the MMC group also showed greater keratometry flattening than the CXL-only group.
The authors concluded that similar studies need to be performed on simultaneous CXL and photorefractive keratectomy to evaluate the role of MMC in haze formation in such procedures.