Online course boosts glaucoma screener numbers
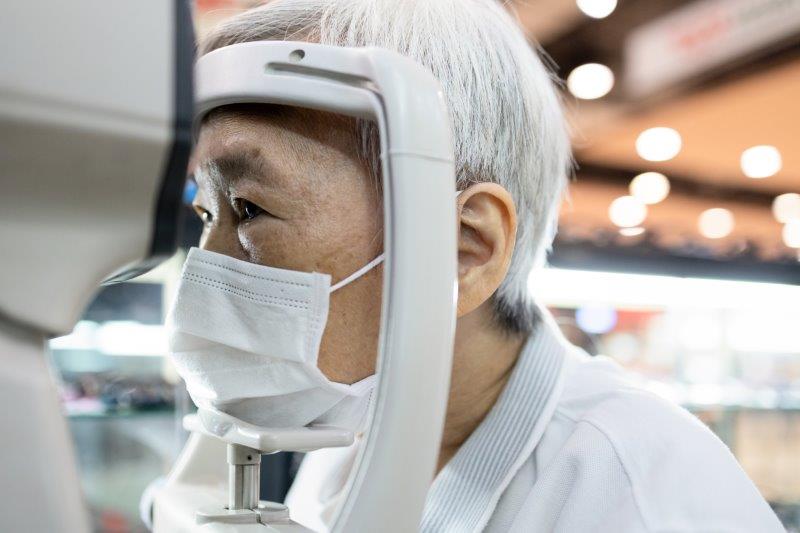
A Vietnamese study has shown how non-ophthalmic healthcare workers could detect signs of glaucoma from retinal images with an accuracy comparable with ophthalmologists after completing a short online course.
The 43 diabetic retinopathy graders – including nurses, technicians and non-ophthalmic physicians – completed a five-hour online course on Cybersight, Orbis's telemedicine and e-learning platform. Testing showed graders’ screening accuracy doubled following the course, putting them on a par with the 29 ophthalmologists who did not take the course, reported the study’s international team.
There is a growing gap between the burden of glaucoma in Asia and the number of trained ophthalmologists, said Ngoc Pham, country director, Orbis Vietnam. “A new screening model that utilises lower-level health workers is necessary to fight this disease in Vietnam, the rest of Asia and beyond."
The full study was published in BMJ Open, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37945295/